NEURONS
Nervous System
- starts with an individual nerve cell called a neuron
How does a Neuron fire?
- Resting Potential: slightly negative charge
- reach the threshold when enough neurotransmitters reach dendrites
- go into Action Potential (fire)
All-or-none response
- the idea that either the neuron fires or it does not - no part way firing
- like a gun
Neurotransmitters
- chemical messengers that a released by terminal buttons through the synapse
Types of Neurotransmitters
Achetycholine (ACH)
- deals with motor movements and memory
- lack of ACH had been linked to Alzheimer's disease
Dopamine
- deals with motor movement and alertness
- lack of dopamine has been linked to Parkinson's disease
- too much has been linked to Schizophrenia
Serotonin
- helps control alertness and arousal
- under supply: depression
- over supply: manic symptoms
GABA (gamma - aminobutytic - acid)
- major inhibitory neurotransmitters
- under supply: leads to tremors, seizures, and insomnia
Glutamate
- major excitatory; involved in memory
- over supply: can overstimulate the brain leading to migraines (this is why some people avoid MSG in food)
Drugs Can Be
- Agonist: make neuron fire
- Antagonist: stop neural firing
- Re-uptake Inhibitors: block neurotransmitters from entering the neuron
Sensory (Afferent)
- take information from senses to the brain
Inter
- take messages from sensory neurons to other parts of the brain or to motor neurons
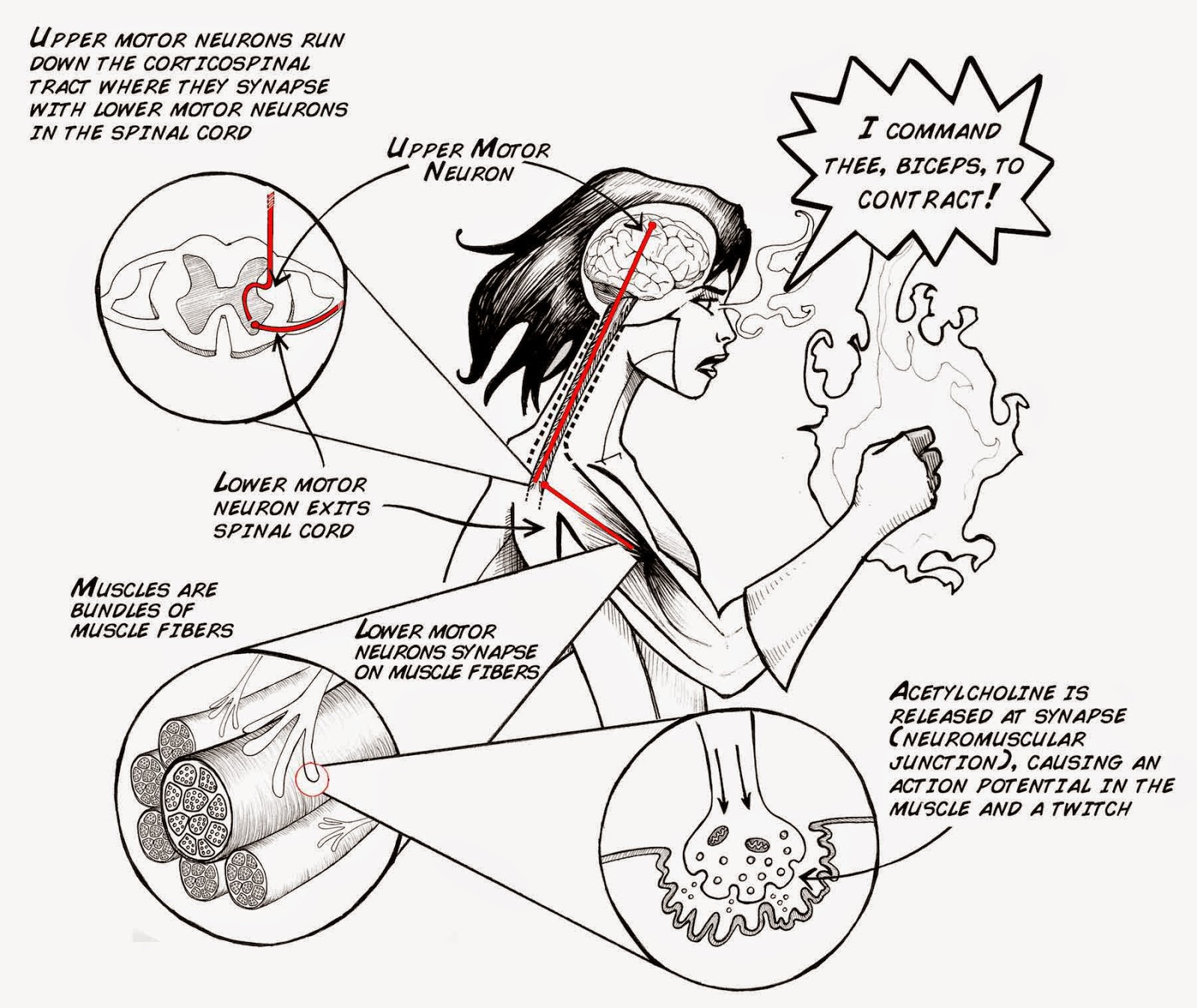
Motor (Efferent)
- take information from the brain to the rest of the body





No comments:
Post a Comment